Towards Open Vocabulary Learning
paper: Towards Open Vocabulary Learning: A Survey(TPAMI 2024)
code: https://github.com/jianzongwu/Awesome-Open-Vocabulary
Concept of Open vocabulary
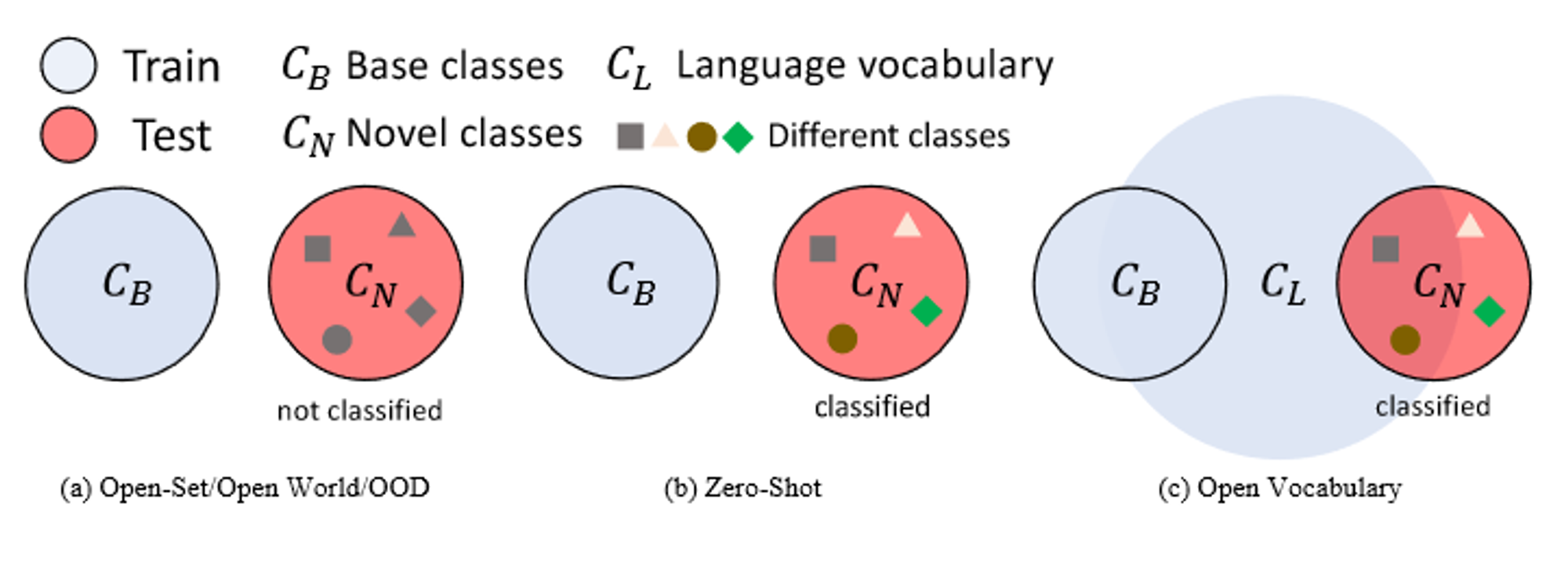
样本分为:base class $C_B$ 和 novel class $C_N$(or out-of-distribution examples)
base class进行training,而novel class没有
open-set, open world, and OOD tasks 在testing 阶段,模型只需要识别novel 类,并标记为unknown,不需要识别特定的类别。
zero-shot 进一步的将novel class分类。因此,更具挑战性。
由于对novel类实际识别性能较低,且image-text pair容易获得,近来工作(21,22)提出open vocabulary,他允许使用有更大的语言词汇(language vocabularies $C_L$)的 额外的低成本训练数据或者预训练视觉语言模型,如clip。
$C_L$可能包含$C_B$ 和 $C_N$的概念,以在novel类中具有泛化性。并不严格要求包含。他可能有在预定义的novel类之外的词汇,因此进一步扩展泛化性。
- Open-Set / Open World / OOD,这三个任务只需要模型从分类中识别和拒绝未知对象。该模型只需要找到未知的类或实例,而不需要将它们划分到不同的类中。
- zero-shot learning。该模型在训练过程中对$C_N$进行了严格的训练,训练过程中$C_B$类不可用。该模型需要预测新对象的具体类别。
- 开放式词汇学习。基于零样本学习设置,可以获得额外的低成本训练源或知识$C_L$,即大规模语言词汇。例如,image caption是最常用的语言数据,可以帮助扩展开放词汇模型的语义空间。人们还可以使用预训练的视觉语言模型,将其用于新颖的类别分类。
Open Vocabulary Learning Based on the zero-shot learning setting, one can acquire an additional low-cost training source or knowledge $C_L$, large-scale language vocabulary. For example, image captions are the most commonly used language data to help extend the semantic space of an open vocabulary model. One can also use the pre-trained vision language models by adapting them for novel class classification.
$C_L$ may contain the concepts of both$C_B$ and$C_N$, which enables model to generalize across novel classes. Note that$C_L$ is not strictly required to contain $C_B$ or$C_N$ , as the language vocabulary may not cover all the class names in the vision data. On the contrary, $C_L$may also have words out of the pre-defined novel categories, which can further extend models’ generalizability.
close-set
能识别训练集中存在的预定义类别
zero-shot learning
使其从已注释(已见)的对象类泛化到其他(未见)的类别。
“Most approaches adopt word embedding projection to constitute the classifier for unseen class classification” (Wu 等, 2023, p. 1) (pdf) 🔤大多数方法采用词嵌入投影来构成分类器,用于未知类别的分类🔤
“As a result, during inference, the model identifies novel classes solely based on their pre-defined word embeddings [9], [10], [11], thereby limiting exploration of the visual information and relationships of those unseen classes.” (Wu 等, 2023, p. 1) (pdf) 🔤因此,在推理过程中,该模型仅根据预先定义的词嵌入来识别新的类,从而限制了对那些未见的类的视觉信息和关系的探索。🔤 这就是为什么ZSL方法已经被证明在新的类中产生不令人满意的结果。
open vocabulary
“the model trains on base classes and inferences on both base and novel classes” (Wu 等, 2023, p. 1) (pdf) 🔤模型在base类上进行训练,在基类和新类上进行推理🔤
zero-shot vs open vocabulary
零样本学习与开放词汇的关键区别在于可以使用与视觉相关的语言词汇数据,如图像标题作为辅助监督。
使用语言数据作为辅助监督的动机是
- 语言数据(文本)标注成本更低
- 语言数据提供了更广泛的词汇量,因此更具有扩展性和泛化性
open vocabulary methods 大多通过利用VLMs(visual language models)学习到的对齐,消除close-set和open-set场景边界。
timeline
Open Vocabulary Video Understanding
动作识别任务
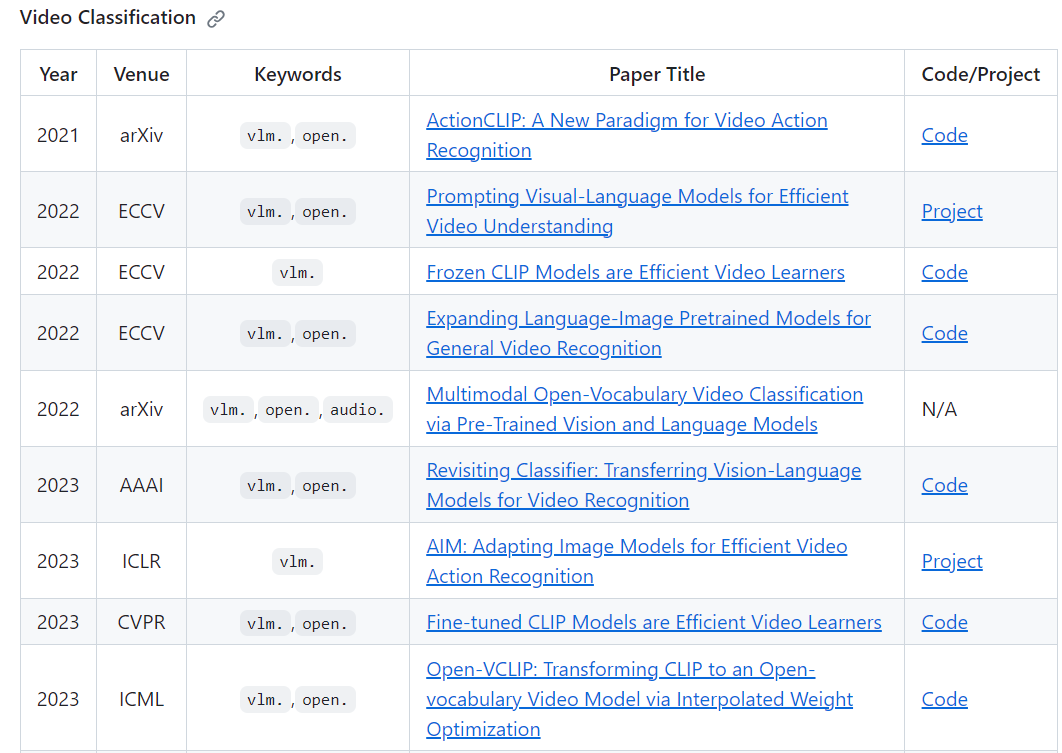

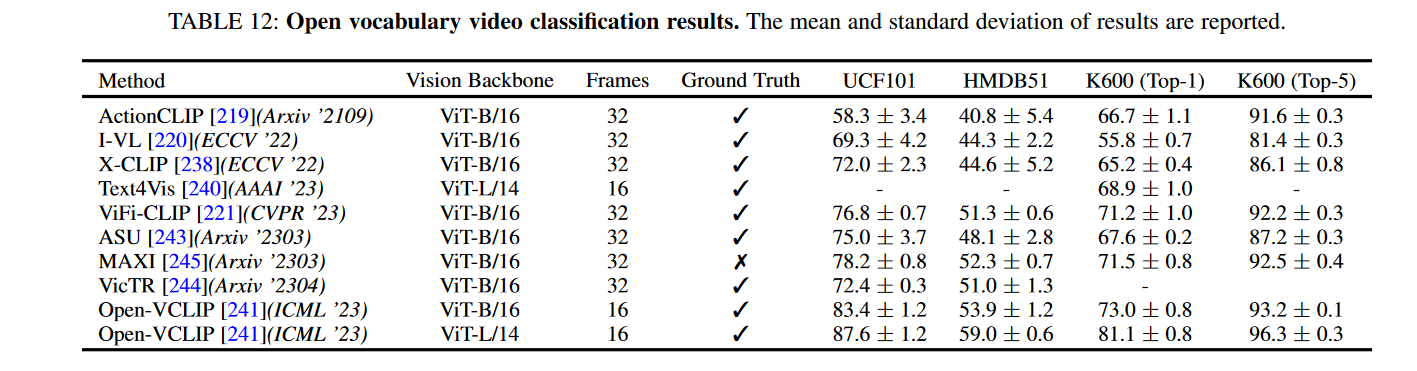
kinetics 400 训练,其他测试
ActionCLIP: A New Paradigm for Video Action Recognition 2021 arxiv
使用基于图像的视觉-语言预训练的知识。它为视频行为识别中的零样本能力增加了一个时间融合层。
Prompting Visual-Language Models for Efficient Video Understanding (ECCV 2022)
通过在一个冻结的CLIP图像编码器顶部训练transformer层,也可以得到类似的范式,并且具有很强的零样本能力。
Frozen CLIP Models are Efficient Video Learners (ECCV2022)
使用冻结的CLIP进行有效的视频行为识别
XCLIP: **Expanding Language-Image Pretrained Models for General Video Recognition (ECCV 2022)**
使用视频编码器,利用编码器中的时间信息进行视频识别。它将来自视频编码器的特征与在基于图像的视觉语言对(例如, CLIP)上预训练的文本编码器进行对齐。
Revisiting Classifier: Transferring Vision-Language Models for Video Recognition (AAAI 2023)
关注于分类器,提出使用CLIP文本编码器作为语义目标进行视频分类。
**Open-VCLIP: Transforming CLIP to an Open-vocabulary Video Model via Interpolated Weight Optimization (ICML 2023)**
Open VCLIP 将CLIP到视频的知识转移建模为一个连续学习问题,并提出插值权重优化来解决该问题。
AIM: Adapting Image Models for Efficient Video Action Recognition (ICLR 2023)
AIM tackles the open vocabulary video classification problem by adding adapt layers on top of the CLIP image encoder.
ViFi-CLIP **Fine-tuned CLIP Models are Efficient Video Learners** (CVPR 2023)
ViFi-CLIP 揭示了一个简单的微调baseline(基于CLIP视觉编码器和时域池化的图像级特征提取)而不是改进的融合层 可以有很强的性能,并进一步研究了prompt tuning的影响。
最近开放词汇视频分类的进展将注意力转向了VLM建模中的语言部分
VicTR: Video-conditioned Text Representations for Activity Recognition (arxiv 2023)
VicTR引入了视频条件文本表示来联合优化视觉和文本信息。
MAtch, eXpand and Improve: Unsupervised Finetuning for Zero-Shot Action Recognition with Language Knowledge (arxiv 2023) MAXI利用LLMs通过文本扩展为视频构建一个无标注的文本包。